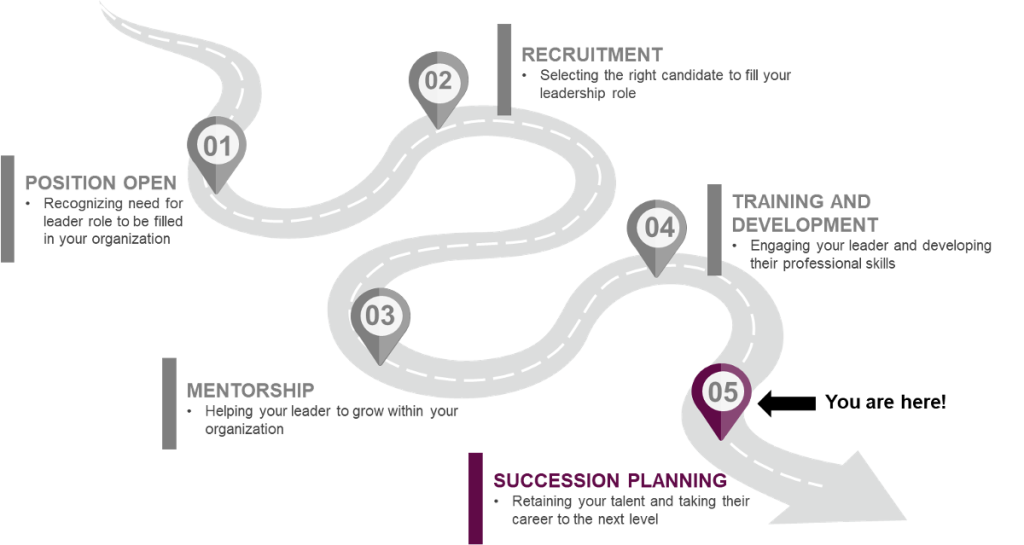
Welcome to Succession Planning!
You are at the final stop in your Leader Journey!
Whether you have hired new talent externally or filled your position internally, succession planning is a key talent process that enables growth and retention.
Succession planning is a primary consideration your organization needs to make to ensure the longevity of your leader pipeline.