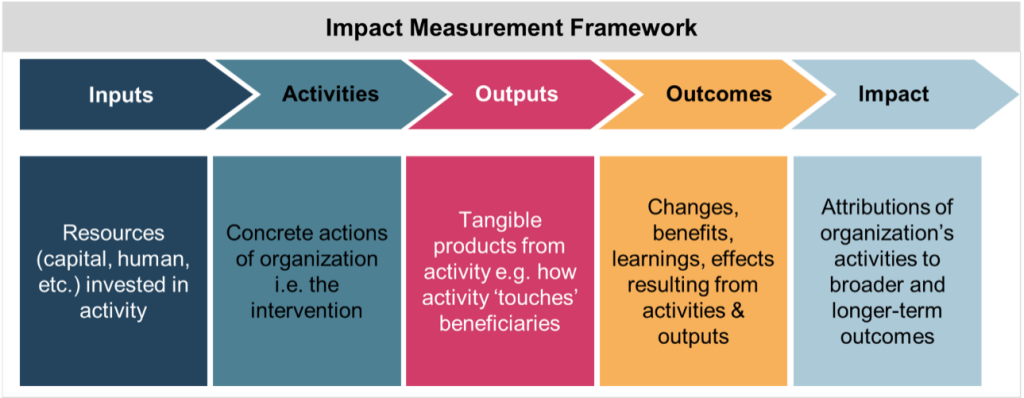
1.2 Training and Development
An important consideration to sustain organizational change is continued education for those who are decision-makers as it takes time to put learned actions and behaviours into practice. Below are two types of training that board members and leaders can participate in to foster an environment focused on respecting the differences of others.
1. Board-Specific Training:
a) Training to help new board members grow and get support they need to succeed
- Recruiting diverse board members is not about “checking a box”; it is about supporting the transition of women and/or non-binary individuals, Racialized, Black, and/or People of Colour, 2SLGBTQ+ and/or gender and sexually diverse individuals, People with disabilities, and “Aboriginal” and/or Indigenous Peoples into board positions
- Finding ways to educate people to be a good board member and support their fellow new board members to be successful is critical to the success of the board
b) Training to align on expectations, behaviours and goals of existing and new board members
2. Formalized EDI Training:
Board members should partake in the following formal EDI training:
- Inclusive leadership training: Training on how to become an inclusive leader
- Unconscious bias training: Training on how to become aware of unconscious bias and how to recognize your own biases